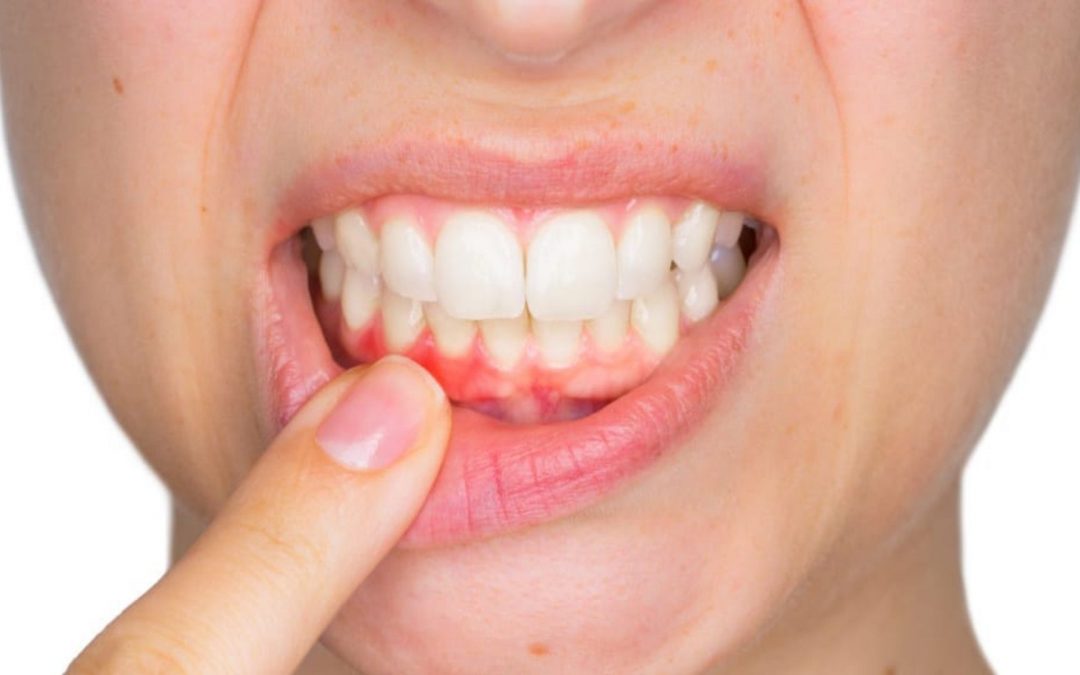
5 Common Causes of Bleeding Gums Yikes, bleeding gums! You may panic a little bit when you are...
5 Common Causes of Bleeding Gums – 2022
read more

5 Common Causes of Bleeding Gums Yikes, bleeding gums! You may panic a little bit when you are...